Working Time
Book Appointment
Peripheral nerve injuries occur when nerves outside the brain and spinal cord sustain damage due to trauma, compression, or various medical conditions. These injuries can result in loss of sensation, muscle weakness, or paralysis in the affected areas. Treating peripheral nerve injuries involves various approaches depending on the type and severity of the injury.
Understanding Peripheral Nerve Injury
Types of Injuries:
Neurapraxia:
Mildest form, involving temporary dysfunction without nerve damage. It often resolves on its own.
Axonotmesis:
Nerve damage without complete severing. Nerve fibers are disrupted but the nerve sheath remains intact.
Neurotmesis:
Most severe, involving complete severing of the nerve, leading to loss of function.
Treatment Approaches
Observation and Conservative Care:
Neurapraxia injuries might heal with time and may not require surgical intervention.
Surgery:
Nerve Repair:
Directly reconnecting the damaged nerve ends to restore continuity.
Nerve Grafting:
Using nerve grafts to bridge the gap between severed nerve ends if direct repair is not possible.
Nerve Transfer:
Rerouting healthy nerves to restore function in more critical areas.
Rehabilitation:
Physical therapy is essential post-surgery to regain strength, mobility, and function in the affected area.
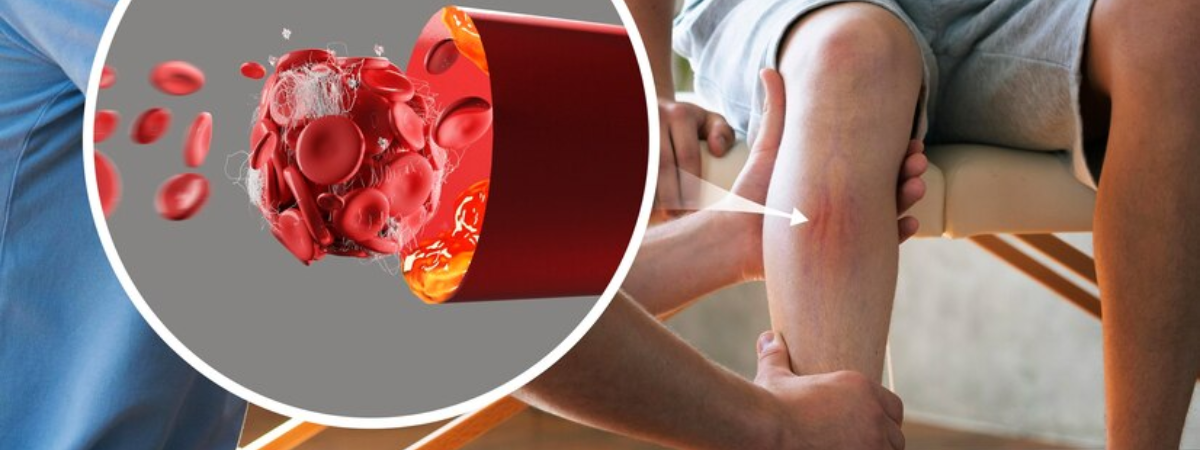

Considerations and Expectations
Recovery Time: The recovery period varies based on the severity of the injury, the success of the surgical procedure, and individual factors.
Rehabilitation Challenges: Complete recovery may not always be achievable, and residual impairment might persist.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consultation with a neurosurgeon or specialist in peripheral nerve injuries is crucial. They assess the injury, discuss available treatment options, and recommend the most suitable approach.
Embracing Recovery and Rehabilitation
Managing peripheral nerve injuries involves understanding treatment options, seeking professional guidance, and committing to a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Embracing this process involves patience, dedication to therapy, and working closely with healthcare providers to maximise recovery potential. While complete recovery might not always be possible, treatment and rehabilitation significantly improve function and quality of life for many individuals affected by peripheral nerve injuries.